If a user who upgraded from Windows 7 to Windows 8 is dissatisfied with the new OS, he can try Uninstall Windows 8 and restore previously installed Windows 7. This manual is based on an article in the Microsoft knowledge base KB971760, which describes a step-by-step procedure for restoring a previously installed Windows OS on a computer.
In addition to KB 971760, we could not find any other official instructions for removing Windows 8 and restoring Windows 7, however, this article, if certain conditions are met and the performer has “direct hands”, will allow even a novice user to manually restore Windows 7 after the computer was installed with Windows 8. The instructions we offered have more than once helped us roll back the installation of Windows 8 (both Preview and RC versions).
Important. You perform the procedure described below at your own peril and risk, taking into account the possible risks of loss of system functionality and important data. In addition, it often happens that Windows restored from the Windows.old folder is unstable. Microsoft does not guarantee that the OS restored in this way will work correctly, and in case of multiple problems, it recommends that you reinstall the version of the OS that you need.
Conditions for restoring a previous version of Windows
So, restoring Windows 7 after installing Windows 8 on top of it is only possible if Windows 8 was installed in update mode ( Upgrade), and not a clean (disk formatted) installation of Windows 8 (Custom Install).
Upgrading from Windows 7 to Windows 8 can be done if the Win 8 installation is running on a running system and the option is selected: Upgrade: Install Windows and keep files, settings and applications.
Important. Before starting the Windows 8 removal procedure, it is recommended to create a backup copy of important data (documents, favorite photos) stored on the disk on which the system is installed.
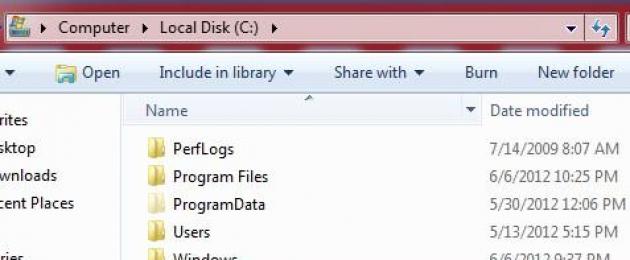
If Windows 8 was installed in update mode, this means that there must be a directory on the system disk Windows.OLD.
This directory, which is automatically created when you upgrade Windows to a newer version, contains files and data from a previous installation of Windows that was installed on the same partition. 
The Windows.old folder must contain the following directories (some directories may be hidden):
- Windows
- Program Files
- ProgramData
- Users
- Program Files (x86) (if 64-bit Windows was installed)

Important. If the Windows.OLD directory is missing (you may have deleted it earlier according to the instructions), rolling back to a previously installed system is impossible.
Estimate the size of the Windows.OLD folder; it should be less than the free space on the C: drive. If the size of the Windows.old folder is two or more times the amount of free disk space, it will most likely not be possible to restore a previously installed Windows.
Procedure for removing Windows 8 and restoring Windows 7
Launching Windows Recovery Environment
Restart your computer and boot from your Windows 7/8 installation disk, bootable Live CD/USB disk, or .
When “” appears, press any key on the keyboard. 
We need to achieve the appearance of a command line in which all operations will be performed.
If you are using an installation disk, click Install Windows(Install Windows), select language, time and click Next.
In the window that appears, click the button Repair your computer in the lower left corner. 
In the window System Recovery Options select any available OS and click Next.
Then run the command prompt by selecting the option Command Prompt.
If you booted according to the described scenario, and the system (Windows 8) was installed on the C:\ drive, then all subsequent operations will be performed in the context of the C: drive. If you booted from a different type of boot disk, then most likely the drive letter will be different. In my example this will be the D: drive.
To change the current drive, run the command
To make sure that this disk is the one we have to work with, you can display its contents using the command
All standard directories located in the Windows root should be displayed, as well as the Windows.OLD folder and custom folders. 
Backing up Windows 8 files
Ren Windows Windows.8 ren “Program Files” “Program Files.8″ ren “Users” “Users.8″ Attrib –h –s –r ProgramData ren “ProgramData” “ProgramData.8”
Ren “Program Files (x86)” “Program Files (x86).8″

Moving the directories of the restored Windows 7 to the root of the system disk
We extract the directories of the restored Windows 7 from the Windows.OLD folder and move them to the root of the system drive:
Move /y d:\windows.old\windows d:\ move /y “d:\windows.old\program files” d:\ move /y d:\windows.old\users d:\ Attrib –h –s –r d :\windows.old\programdata move /y d:\windows.old\programdata d:\
For 64 OS also run the command:
Move /y “d:\windows.old\program files (x86)” d:\
Important: if the system is located on a different drive, replace drive D: with the name of your drive, for example C:

Restoring the boot sector of a previously installed Windows 7
Go to the Windows installation disk (there may be a little difficulty here, since the initial drive X:\ is not the original Windows installation disk, it is a disk with the WinRE environment). In my case, the CD drive with the Windows 7 distribution was assigned to drive E:. Change the current disk with the command:
The following command will display a list of files and folders on the disk, if they include boot, bootmgr, setup.exe, sources, upgrade, etc., then you have selected the correct disk.
Using the bootsect command, we will restore the boot loader of the previous version of Windows:
Boot\bootsect/nt60 D:
Important: Replace D: with the name of your system drive.

Now you need to type the command exit and restart your computer. After rebooting, remove the Windows installation disk, after which the system should boot into the restored Windows 7.
In the event that you need certain files or folders from Windows 8 that we removed, they can be found on the system drive in directories with the suffix .8 .
All that remains is to delete the Windows 8 boot entry in the boot loader menu. To do this, run the program msconfig, go to the tab Boot, select the Windows 8 (recovered) entry (C:\Windows.8), click Delete, Apply, and then OK. 
Check the functionality of the restored Windows 7 (it is likely that there will be problems with the operation of some installed programs).
To clear the system disk of files left over from Windows 8, you must run the following commands sequentially:
Rd windows.old /s /q rd windows.8 /s /q rd “program files.8″ /s /q rd users.8 /s /q rd /$windows.~bt /s /q exit
We hope this guide on how to remove Windows 8 and restore Windows 7 from the Windows.OLD folder will be useful.
During the operation of the operating system, various problems may arise that will lead to incorrect operation of the computer. Typically, in this case, users simply reinstall Windows from scratch. This is a correct and reliable method, but very long. You will need to find an ISO image on the Internet, create a bootable USB flash drive, install the OS, find and install all the necessary drivers and programs necessary for operation. This article describes an alternative method - how to restore your Windows 7 system without a long reinstallation and special disks.
When to restore
The need for recovery appears when the Windows operating system begins to work incorrectly. Perhaps, after a virus attack, your computer began to take a long time to load or slow down. Or you installed low-quality drivers on the disk, which caused problems with the operation of certain programs.
Some users may accidentally delete important files or registry entries, which also leads to various problems. When installing complex programs, a failure may occur, which will disrupt the normal operation of the system.
In short, if the operating system starts to work slowly, takes a long time to load, certain programs stop running, glitches, freezes and graphic artifacts occur - you need to restore Windows 7.
Benefits of Recovery
Reinstalling the OS is too long a journey. Many users work with complex and cumbersome programs that will need to be reinstalled. You should add drivers for all devices, printers, and so on. For experienced users who know where and what to download, all this takes more than 2 hours. 
The situation is even worse for those users who have only 1 hard drive on their personal computer, not divided into virtual partitions. When reinstalling the OS, the disk must be formatted. This means that you will have to save all important documents, photos and video files, portable programs and installers to external media or cloud storage. If several tens or hundreds of gigabytes of valuable information have accumulated, this can become a serious problem.
On the other hand, recovery does not require any unnecessary operations. You launch it - and after 10-15 minutes you get a fully working Windows system. Unless you have to re-install programs that were not in the version of the OS to which you are “rolling back”. In the meantime, the OS is being restored, you can calmly go about your business.
Restore point
In a special directory on their hard drive, users can make a so-called restore point. This is a special type of file that records data about the current state of the system. Saved configurations, registry entries, a list of installed programs and their settings - Windows adds all this to this list.
Please note that all user data will not be saved. If you accidentally deleted something important, or viruses damaged your documents or photos, restoring Windows 7 will not help you in any way. You should make backup copies of important information separately, saving it to a flash drive or disks, as well as to cloud storage.
The operating system has its own schedule, according to which it scans the contents of the hard drive and creates rollback points. In addition, such backups are made if you install new drivers or large and complex programs that greatly change the OS settings.
All data that characterizes the current state of Windows is saved so that users have the opportunity to undo all recent changes. You can also create such backups manually at any time when it is convenient for you. It is strongly recommended to do them every time before installing any application or after successful installation.
How to make a restore point
Although the system can back up its configurations, it is recommended to sometimes create your own revert points. This way you can be sure that you will always have something to fall back on. The best option is to make one point immediately after installing Windows on your hard drive, drivers and all the necessary programs. And then make separate copies before installing new applications.
Users will need to do the following:

Running System Restore
If you notice that Windows 7 is not working correctly, you can restore to one of the saved states. To do this, you will need to open the System Properties menu again, the System Protection tab, as described in the previous part of the guide.

“I explained that if it detects boot problems, Windows 7 automatically launches the Startup Repair Tool, which performs diagnostics with little or no user intervention and, in many situations, allows you to repair an unbootable system.
After this article was published, many users shared in the comments their less than satisfactory experiences using Startup Repair in . On the other hand, many wrote on the contrary that it helped them restore normal operation of the system. For those unlucky, I would like to remind you that Startup Repair only solves some problems, including missing and damaged system files.
As I mentioned in the previous article, if Startup Repair fails to fix the problem, it displays a System Recovery Options menu with a list of tools you can use to diagnose and restore your system. In this article, I will tell you how to call this menu yourself and describe each tool presented in it.
Calling the “System Recovery Options” menu
You can access the System Recovery Options menu in different ways, depending on your specific situation.
If Windows still starts to boot, you can try to access the System Recovery Options menu manually from your hard drive.
. If Windows doesn't even start to boot, you can call up System Recovery Options by booting your computer from the Windows 7 installation DVD.
. If you have a System Repair Disc, boot your computer from it and open the System Recovery Options menu. I'll tell you about creating a system repair disk another time.
Let's say Windows starts loading, but doesn't finish. To access the System Recovery Options menu in this situation, turn off the computer and then turn it on again. After the initial boot, when you hear a beep indicating that Windows is starting to boot, press and hold the key.
The Advance Boot Options screen appears (Figure A). Select the Repair Your Computer option. As the description at the bottom of the screen suggests, this option displays a list of tools that can be used to diagnose, fix boot problems, and restore the system. To continue, click .
Figure A: Pressing the key when Windows starts to boot brings up the More Boot Options screen.
A message appears telling you that Windows files are downloading, followed by a download screen with a green progress bar. After a while, a dialog box will open asking you to select a keyboard input method (Figure B). Click Next.

Figure B: If you are using English, simply click Next.
The login window shown in Fig. 1 will appear. C. Use an account with administrator rights to log in.

Figure C: Use an account with administrator rights to log in.
After this, the “System Recovery Options” menu will appear, shown in Fig. D.

Figure D: The System Recovery Options menu lists tools you can use to diagnose, fix boot problems, and perform system recovery.
Options
As you can see, there are five options in the System Recovery Options menu. Let's take a closer look at them.
. “Startup Repair”. If this tool does not start automatically when the download fails, it should be used first. Please note that it only fixes some problems, such as missing or corrupt system files. This tool does not correct hardware malfunctions - for example, a hard drive.
. "System Restore". This tool allows you to restore Windows system files to a previous state without in any way affecting your data files - emails, documents, photos. To provide this capability, the utility constantly monitors the state of the operating system for significant changes, which include the installation of applications, drivers and updates. If such a change is anticipated, the utility automatically creates a restore point - essentially a snapshot of the system state, including important system files and certain registry fragments. System Restore stores several different restore points at once, which allows you to roll back the system to any of the saved states. Therefore, “System Restore” can also be used in case of boot failures - just select the latest restore point.
. “System Image Recovery”. If for some reason System Restore doesn't work, and you have a relatively recent image of the operating system on your hard drive, you can restore Windows from it. The system image includes all system files and settings, programs and user files. Please note that the entire system is being restored from the image, so all current programs, settings and files will be replaced by previous versions saved at the time the system image was created.
. "Windows Memory Diagnostic" If, in addition to boot problems, you encounter application and operating system crashes or STOP errors, you can use the Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool to check your RAM modules for problems. The diagnostic tool writes specific values to memory and then reads them back to ensure that the data has not changed.
. "Command Prompt" When you select this option, various command line utilities are available for diagnosing and restoring your system.
What do you think?
In future articles, I'll talk more about the tools in the System Recovery Options menu. Have you ever used them? Share your experience in the comments!
When problems arise with the operating system, sometimes situations occur in which system recovery does not work. Many of us have found ourselves in situations where, for some reason, we needed to restore the operating system.
This is the easiest way to fix any problems in the computer's operating system or problems associated with the operation of certain programs.
You start the operating system recovery process and see that System Restore does not work in Windows. The operating system recovery process starts, goes through all recovery stages, and at the end of the process you see, instead of a window with information that the system was successfully restored, a window with information that the system could not be recovered.
Why System Restore Doesn't Work
If system restore is not disabled, then the reason why system restore does not work may be the antivirus installed on the computer.
To solve this problem, you need to disable your antivirus self-defense. This incident also happened to me. I also needed to do an operating system restore, but the operating system restore did not happen. In my case, the cause was Kaspersky Anti-Virus 2012. There were no such problems with earlier versions of this anti-virus.
Restoring the operating system only works if performed in “safe mode”. If you restore the operating system in normal mode, if you simply pause the antivirus protection, it will not work; at the very end of the operating system restoration process, you will see a message that the operating system was unable to restore the system to an earlier state.
To solve this problem in Kaspersky Anti-Virus, you need to go to “Settings” => “Advanced settings” => “Self-Defense”. In the “Self-Defense Options” tab, you need to uncheck the box next to “Enable Self-Defense”, and then click on the “OK” button.
After these steps, you can begin restoring the operating system.
After the operating system recovery is complete, the antivirus is turned on automatically.
Keep in mind that this is only one of the possible reasons.
Conclusions of the article
System Restore may not work due to the self-defense of the antivirus installed on the computer.
Often, users are faced with the problem of the operating system freezing or even becoming infected with viruses. Before resorting to radical methods to solve this problem, this means reinstalling the system, it is worth trying to solve the problem by restoring it.
In general, system recovery is usually divided into three types:
- System rollback, that is, its restoration to a previous state.
- Restoring the system using the installation disk
- Recovering individual files if they are damaged
Each of these methods has its own pros and cons, and for each specific case you need to make your own decision about which method to restore the system. Let's start in order.
System rollback
The developers of Windows 7 took into account the fact that some programs may not work correctly, and even after they are removed, some files may remain that interfere with the stability of the operating system. In this regard, a system rollback feature was added to Windows. The network of this action is that during the operation of the computer, control points are created. If the need arises, the user has the opportunity to return the state of the computer to the state it had at the time this checkpoint was created. Depending on the Windows distribution from which the installation took place, checkpoints can be created automatically or manually.
Advice
After installationWindowsIt is recommended to enable automatic checkpoint creation if it is not enabled. Because of this, the operating system will take up more space, but it will be possible to avoid the need to reinstallWindows.
When using this method, it is worth considering that all files and changes made to them after the checkpoint was rolled back may be deleted or partially undone.
Advice
Before performing a system rollback procedure, it is recommended to save all important information to a flash drive, since after a rollback it may be lost.
To perform a Windows restore operation through a system rollback, you need to open the Start menu and start typing “System Restore” in the search field. In the pop-up window, select the appropriate item.
The System Restore Wizard will now open. In the first window we click the “Next” button. At this point, we confirm that we are going to restore the system, and also that we are aware of the consequences this may have.

A window opens in which we are asked to select one of the control points to which the rollback will actually occur. Choose the point at which the computer was definitely working stably and without freezes, otherwise the procedure may not help.

After this, you need to confirm that the control point was chosen correctly. If you are sure that you did everything correctly, click the “Next” button.

Then a window will appear warning that system recovery will now begin, and that it cannot be interrupted while it is underway. Click the “Yes” button, after which system recovery will begin.

Upon completion, the computer will automatically reboot. Then a message will be displayed on the screen indicating that the restoration was successful.

note
If the system refuses to boot, you can try restoring the system from safe mode. To do this, when you turn on the computer, press the “F8” key (on some computers the key may be different) until a special menu appears prompting you to select a boot mode. Here, Safe Mode is selected, after which all the above steps are performed.

Restoring the system using a boot disk or flash drive
In some cases, normal system recovery using the built-in program may not be possible. This happens when Windows reboots cyclically, for example, when a system update was interrupted for some reason. As a result, it will not be possible to start Windows not in safe mode, not in normal mode. Then it is possible to restore the system only if you have a boot disk or flash drive.
note
Restoring the system using a disk or flash drive should be done from the same distribution from which the installation took place. This ensures that there are no recovery problems associated with different system settings and versions.
To carry out this operation, you will need to write the Windows distribution onto a disk or flash drive and connect it to the computer. In the Bios settings, put it in first place. After downloading the installation and recovery program, the following steps are performed:
1. On a black background, we are asked to press any button to boot from disk, which is done.

Advice
It is better to press the spacebar or “Enter”, as some keys may not be recognized.

3. Select "System Restore"

4. In the window that opens, confirm the system language.

5. A window will open in which you need to select an option offering to restore the system

6. Wait for the recovery to complete, after which the computer will reboot.
7. In the BIOS you set the boot priority to the hard drive and see the result. If everything went well, the system will start.
Note.
Restoring a system from a disk is a rather long process that can take from half an hour to several hours. In addition, this method will not help with damage to the boot sector.
Recovering some system files and other problem solutions
There are times when a full system recovery is not required, but you just need to replace or add a file. Below are two similar examples and ways to solve them.
1. A virus that requires you to transfer money to the attacker’s wallet or simply does not allow you to boot the system. Until recently, these were one of the most common viruses, but now their number is decreasing every year. Before transferring money to someone or reinstalling the system, try downloading and running the Dr.Web Live CD program. It will scan all hard drives and remove the annoying virus, and at the same time clean the entire remaining computer of all possible threats.

Advice
Even if you do not encounter such a problem, it is recommended to run your computer with Dr.Web Live CD or its equivalent once every three months, because some viruses can bypass your antivirus.
2. One of the most common and at the same time unpleasant problems with system booting is the message “BOOTMGR is missing. Press Ctrl + Alt + Del to restart." This means that the boot sector has become corrupted, and as a result the operating system cannot boot. The solution to this problem is quite simple. Make a bootable flash drive with the MbrFix program or its equivalent. Then start the computer, having previously configured the BIOS to boot from a flash drive and run the program. It will automatically fix the problem and restore system functionality.

The choice of recovery method is different for each case. Unfortunately, in some cases it may be impossible to restore the system's functionality. In this case, only a complete reinstallation of Windows can solve the problem.
- In contact with 0
- Google+ 0
- OK 0
- Facebook 0